Alcohol’s Role in Heart and Lung Disease
Introduction
Alcohol is widely consumed around the world in social settings, celebrations, or as a means to relax. While moderate drinking may not cause harm for some people, heavy or long-term alcohol use can have serious effects on your health. Two of the most impacted organs are the heart and the lungs. Understanding how alcohol affects these vital organs can help people make informed choices about their drinking habits.
1. How Alcohol Affects the Heart
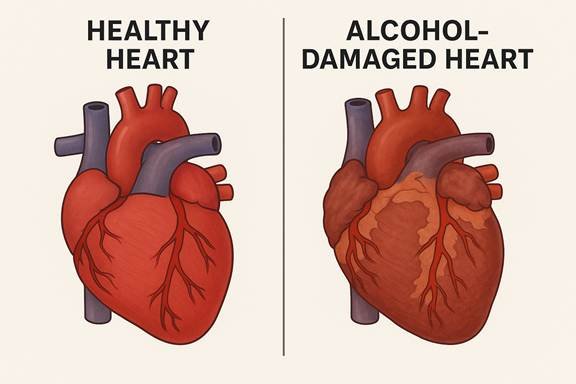
– Weakens the Heart Muscle (Cardiomyopathy):
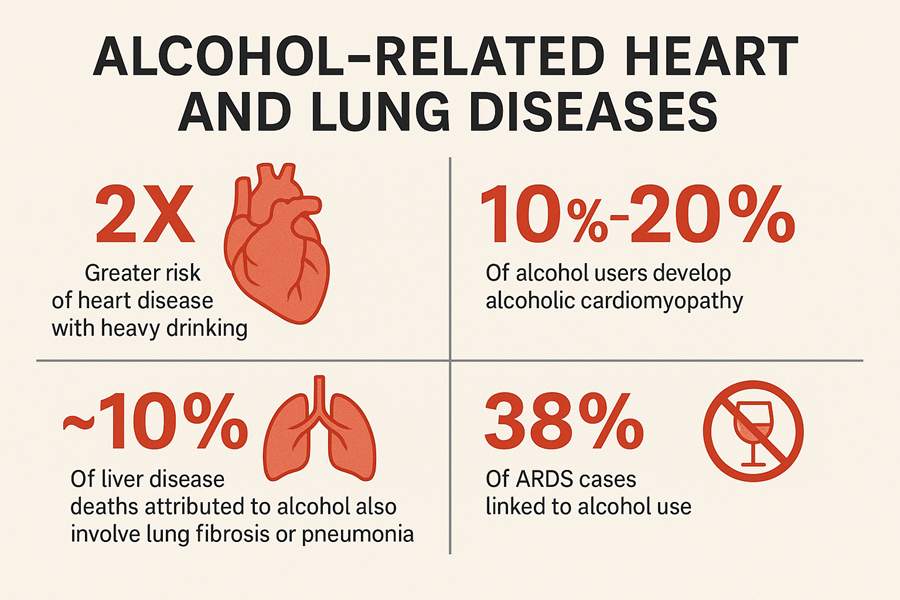
Heavy drinking can weaken the heart muscle, making it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently. This condition is known as alcoholic cardiomyopathy and can lead to heart failure.
– Irregular Heartbeat (Arrhythmias):
Even a single episode of heavy drinking can lead to irregular heart rhythms like atrial fibrillation. This can increase the risk of stroke and other heart problems.
– High Blood Pressure:
Alcohol raises your blood pressure. Over time, high blood pressure can damage your arteries and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
– Increased Risk of Heart Disease:
Long-term alcohol use increases the chances of developing coronary heart disease, especially when combined with other risk factors like smoking, poor diet, or lack of exercise.
2. How Alcohol Affects the Lungs
– Weakens the Immune System:
Alcohol reduces the body’s ability to fight off infections. This can make the lungs more vulnerable to illnesses like pneumonia and tuberculosis.
– Increases Risk of Lung Infections:
People who drink heavily are more likely to get serious lung infections. This happens because alcohol impairs the protective reflexes that keep harmful bacteria and viruses out of the lungs.
– Slows Breathing:
In high doses, alcohol can slow down the breathing rate. This can be dangerous, especially if someone passes out after drinking too much.
– Worsens Chronic Lung Conditions:
For people with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), alcohol can make symptoms worse and increase the risk of complications.
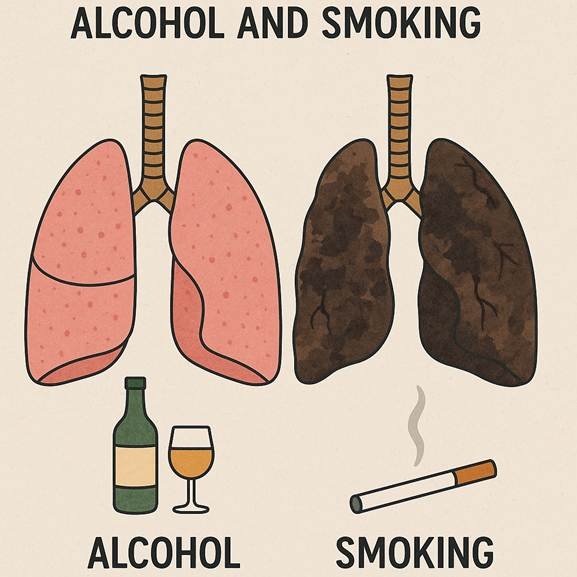
3. The Link Between Alcohol, Smoking, and Lung Disease
Many people who drink heavily also smoke. The combination of alcohol and smoking can be especially dangerous. Smoking damages the lungs, and alcohol weakens the immune system. Together, they significantly increase the risk of lung cancer, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema.
4. Can Moderate Drinking Be Safe?
– Light to Moderate Drinking:
Some studies suggest that light drinking (like one glass of wine per day) may have heart benefits for certain people. However, the risks can outweigh the benefits, especially if someone has existing health issues or drinks more than the recommended limits.
– Individual Differences:
Everyone’s body reacts differently to alcohol. Age, gender, weight, and family history all play a role in how alcohol affects your health.
– Safer Choices:
The safest choice for heart and lung health is to drink alcohol in moderation or not at all. People with health conditions should talk to their doctor about whether it’s safe for them to drink.

Conclusion
Alcohol can have a serious impact on your heart and lungs, especially when consumed in large amounts over time. It can weaken your heart, raise your blood pressure, increase your risk of infections, and make existing health problems worse. Making smart choices about alcohol can help protect your vital organs and improve your overall health.
Role of Naturopathy in Heart Diseases
5 Common Stress Busters for Better Heart Health
5 Disadvantages of Substance Abuse
How Drugs Lead to Depression
5 Common Side Effects of Drugs in Youngsters
The Importance of 5 ‘C’s in De-addiction
How to Quit Alcohol: A Step-by-Step Guide
5 Effective Ways to Quit Smoking
5 Main Causes and Symptoms of Heart Failure
Preventive Cardiology – A Life Saviour Approach
The Role of Laughter Therapy in Healing Diseases
Office Stress Causing Heart Attacks – A Myth or Reality?
5 Super Foods for a Healthy Heart
Alcohol’s Role in Heart and Lung Disease
The Dangerous Link Between Tobacco and Lung Diseases
Top 5 Yogas to Reduce the Danger of Heart Attacks
How Yoga is Helpful in Curing Heart Diseases
Top 5 Reasons to Visit a Cardiologist
5 Essential Tips for Diabetes Control in Heart Patients
The Role of Alcohol & Tobacco in Heart Disease
The Connection Between Obesity and Heart Diseases
How to Perform CPR: Guidelines, Procedures & Ratio
❤️ 5 Easy Ways to Improve Your Heart Health
5 Main Causes and Symptoms of Heart Failure
All Categories
- Health (30)
- Life Style (1)
Must read Recent Blogs
Top 5 Yogas to Reduce the Danger of Heart Attacks
Top 5 Reasons to Visit a Cardiologist
The Role of Laughter Therapy in Healing Diseases
The Role of Alcohol & Tobacco in Heart Disease
The Importance of 5 ‘C’s in De-addiction
The Dangerous Link Between Tobacco and Lung Diseases
The Connection Between Obesity and Heart Diseases
Role of Naturopathy in Heart Diseases
Preventive Cardiology – A Life Saviour Approach
Office Stress Causing Heart Attacks – A Myth or Reality?
How Yoga is Helpful in Curing Heart Diseases
How to Quit Alcohol: A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Perform CPR: Guidelines, Procedures & Ratio
How Drugs Lead to Depression
Alcohol’s Role in Heart and Lung Disease
5 Super Foods for a Healthy Heart
5 Main Causes and Symptoms of Heart Failure
5 Main Causes and Symptoms of Heart Failure
5 Essential Tips for Diabetes Control in Heart Patients
5 Effective Ways to Quit Smoking
5 Disadvantages of Substance Abuse
5 Common Stress Busters for Better Heart Health
5 Common Side Effects of Drugs in Youngsters
❤️ 5 Easy Ways to Improve Your Heart Health







